3 Ways to Calculate P-Value in Excel Easily
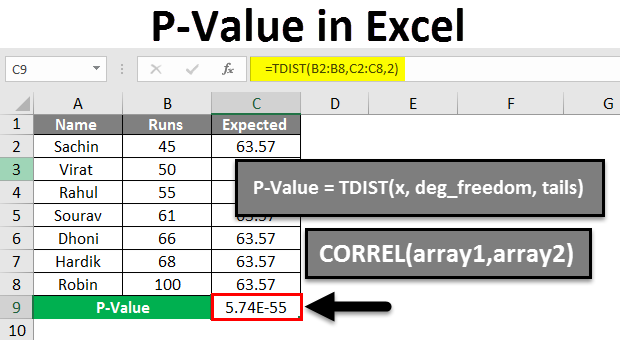
The P-value is a fundamental statistical measure often used to determine the significance of results from hypothesis testing. Excel, a widely available and versatile tool, offers several methods for calculating P-values, making it accessible even to those who are not statistical experts. This post will explore three easy and effective methods to compute P-values in Microsoft Excel, guiding you through each step to ensure you can apply these techniques accurately.
Method 1: Using the T-Test

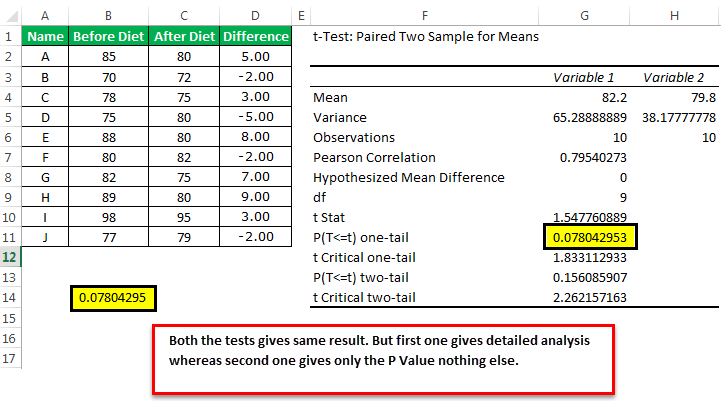
One of the simplest ways to calculate a P-value in Excel involves using the T.TEST function, which is ideal for comparing two sets of data to see if their means are statistically different. Here’s how to do it:
- Step 1: Ensure your two sets of data are arranged in separate columns or rows. For example, let’s say you have two groups of data, Group A and Group B, in columns A and B respectively.
- Step 2: Use the T.TEST function by entering the following formula:
=T.TEST(array1, array2, tails, type)Where:array1is the first data range (e.g., A1:A10)array2is the second data range (e.g., B1:B10)tailsspecifies if you're doing a one-tailed (1) or two-tailed test (2)typedetermines if you want a paired (1), homoscedastic (2), or heteroscedastic (3) t-test
- Step 3: After specifying these parameters, press Enter. The P-value will be displayed in the cell where you entered the formula.
💡 Note: Remember that Excel uses 1 for a one-tailed test and 2 for a two-tailed test. Choose based on your hypothesis.
Method 2: Z-Score and Normal Distribution

This method is particularly useful when you’re dealing with large sample sizes where the central limit theorem applies, assuming the data is normally distributed. Here’s how to proceed:
- Step 1: Calculate the mean and standard deviation of your dataset.
- Step 2: Determine the Z-score for your hypothesis test. If you're testing a null hypothesis where μ₀ is your hypothesized population mean, then the formula for Z-score is:
Z = (x̄ - μ₀) / (σ/√n)Where:x̄is the sample meanμ₀is the hypothesized population meanσis the standard deviationnis the sample size
- Step 3: Use Excel's
NORM.S.DISTfunction to find the P-value:=NORM.S.DIST(-Z, TRUE)This function gives the cumulative normal distribution from -infinity to Z, which for a two-tailed test you would multiply by 2.
| Sample Mean (x̄) | Hypothesized Mean (μ₀) | Sample Size (n) | Standard Deviation (σ) | Z-Score | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 48 | 100 | 2 | 10 | 0.17 |

Method 3: Chi-Square Test for Independence
When you’re looking to test the independence of two categorical variables, the Chi-Square test is your go-to method. Here’s how to implement it in Excel:
- Step 1: Create a contingency table of your categorical variables. Let’s assume you have two variables, Variable X and Variable Y, with categories A, B, C, and D, E, F respectively.
- Step 2: Use the
CHISQ.TESTfunction:=CHISQ.TEST(actual_range, expected_range)Where:actual_rangeis the range containing your observed frequenciesexpected_rangeis where you'll calculate the expected frequencies
- Step 3: Calculate the expected frequencies for each cell by multiplying the row and column totals and dividing by the overall total.
- Step 4: Apply the Chi-Square test formula in Excel to get your P-value.
The P-value can now be interpreted to assess if there is a significant association between your variables. If P-value is below a certain threshold (typically 0.05), you might reject the null hypothesis of independence.
To conclude, calculating P-values in Excel, whether for t-tests, z-tests, or Chi-Square tests, can be straightforward with the right approach. These methods help you make data-driven decisions by quantifying the likelihood of your observations occurring by chance alone. Understanding and correctly interpreting P-values can lead to more robust conclusions from your data analysis, enabling you to confirm or refute hypotheses with statistical rigor.
What is a good P-value for rejecting the null hypothesis?
+
Generally, a P-value of less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant, allowing you to reject the null hypothesis with a reasonable level of confidence.
Can Excel calculate P-value for non-parametric tests?

+
Yes, for non-parametric tests like the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, you can use Excel’s RANK, SUM, and COUNT functions to calculate ranks and then apply formulas to derive P-values.
Is a low P-value the only indicator of a strong relationship between variables?

+
No, a low P-value indicates that the observed effect is unlikely due to chance, but it doesn’t measure the strength or practical significance of the relationship. Consider effect size and confidence intervals too.