Mastering Random Numbers in Excel: A Simple Guide
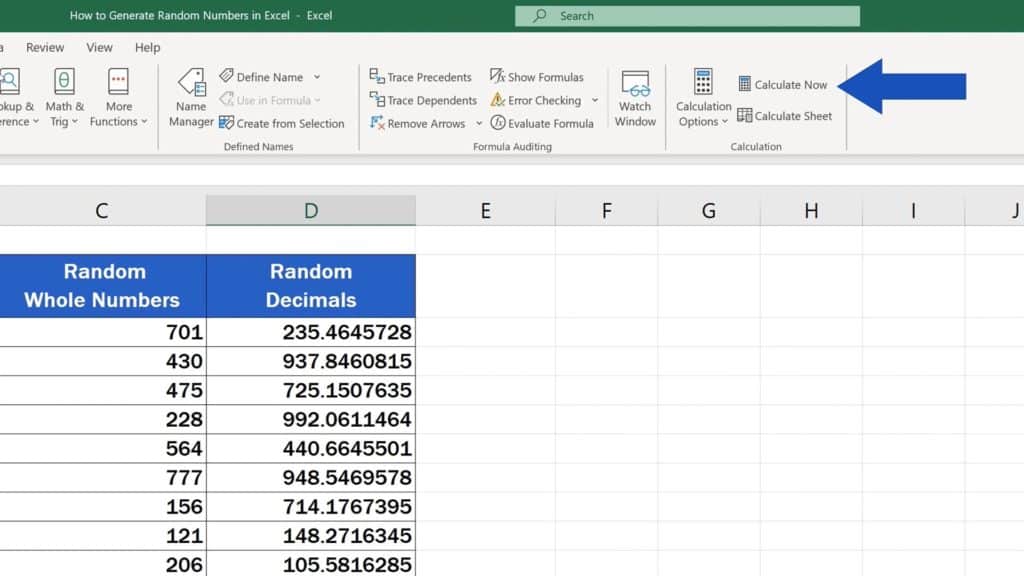
Understanding Random Numbers in Excel
Excel, Microsoft’s powerful spreadsheet software, has built-in capabilities to generate random numbers, which can be immensely helpful in various tasks ranging from simulations to data analysis and education. This guide will walk you through the process of generating, using, and manipulating random numbers in Excel.
Basic Function: RAND
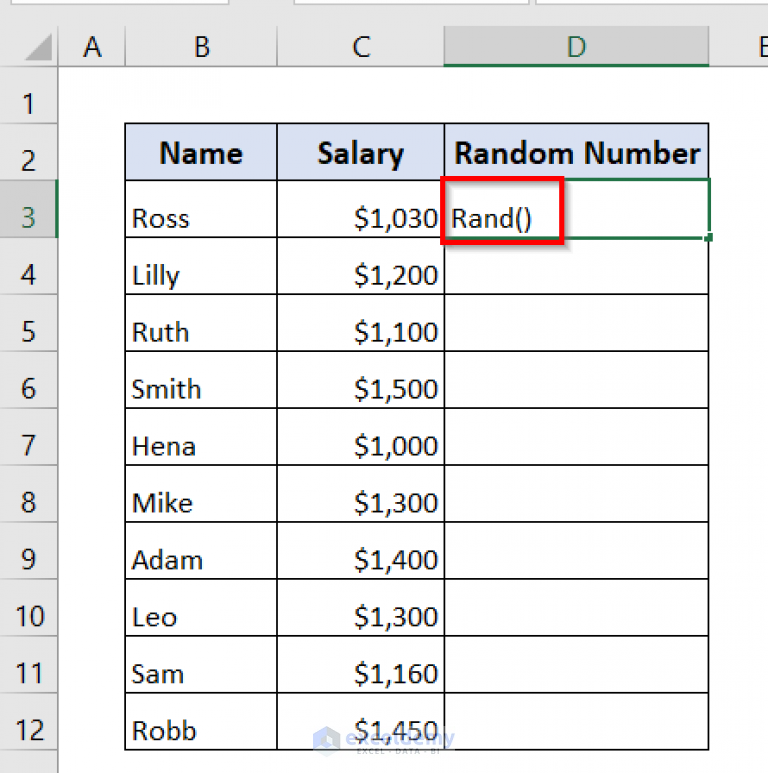
Let’s start with the simplest function for generating a random number in Excel, which is RAND. Here’s how you can use it:
- Open Excel on your computer.
- Select a cell where you want the random number to appear.
- Type =RAND() into the Formula Bar and hit Enter.
The RAND function will return a random number between 0 and 1. Each time you refresh or recalculate the worksheet, this number will change.

✅ Note: The RAND function is volatile, meaning it recalculates every time there's a change in the workbook. This can be useful for simulations but might slow down complex sheets.
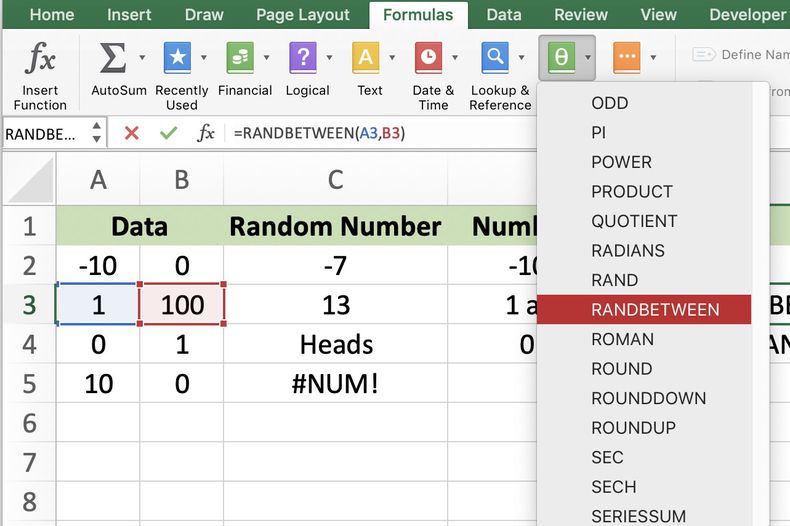
Advanced Functions: RANDBETWEEN
For scenarios requiring a random integer between two specific numbers, the RANDBETWEEN function comes in handy:
- Open Excel on your computer.
- Select a cell where you want the random integer to appear.
- Type =RANDBETWEEN(bottom, top), where bottom and top are the smallest and largest integer values you need.
- Hit Enter to get a random integer between these two values.
Example
| Cell | Formula | Output |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =RANDBETWEEN(1,10) | 8 |
📝 Note: Like RAND, RANDBETWEEN is volatile and will recalculate with any change to the worksheet.
Controlling Randomness
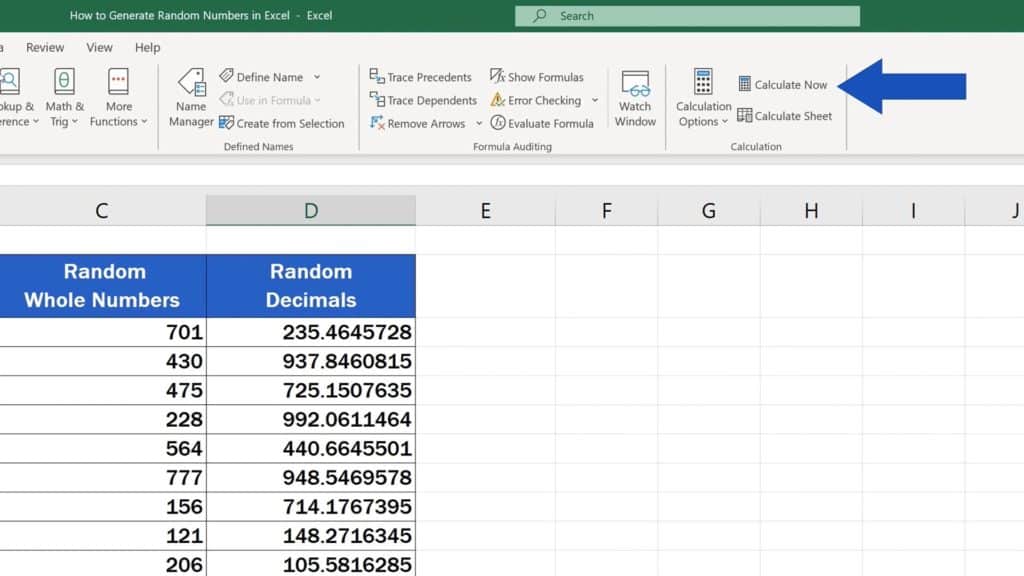
If you need more control over the randomness or wish to avoid recalculations:
Using Random with Other Functions

- INT(RAND() * (High-Low+1))+Low - This formula gives you control over the range while ensuring the result is an integer.
- INDEX(array, RANDBETWEEN(1,COUNTA(array))) - This picks a random element from an array or list.
Generating Unique Random Numbers
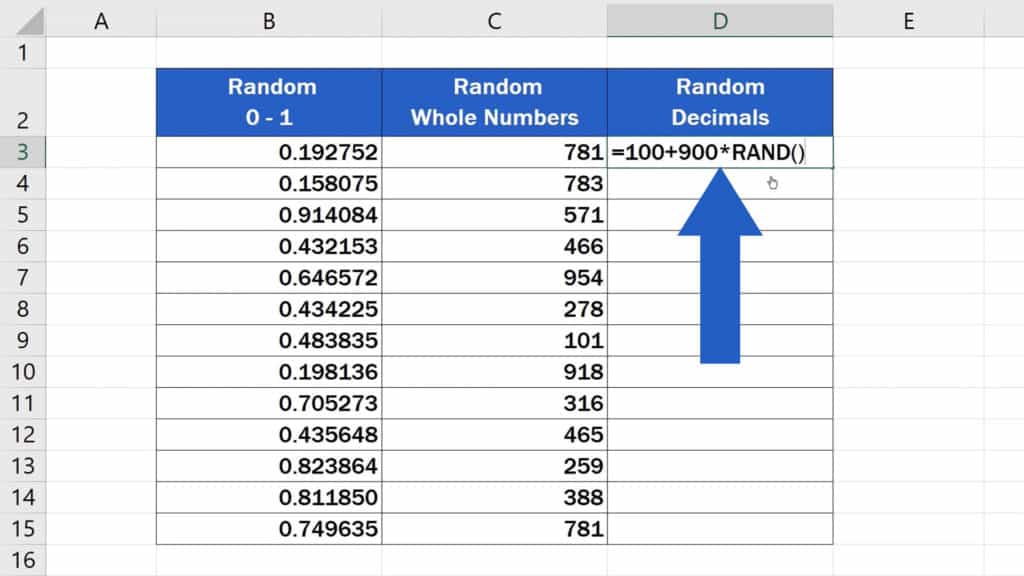
To ensure numbers are unique, you can combine Excel’s functions:
- Enter the formula =RAND() into your range.
- Sort this range by the random numbers.
- The sorted list will be in a unique random order.
Application Examples
Random Sampling

To perform random sampling:
- Enter your data into Excel.
- Create a new column with =RAND() next to your data.
- Sort the data by the random column.
- Select your desired sample size from the top of the sorted list.
Simulations

For simulations or Monte Carlo methods, random numbers are essential. Here’s how you might use them:
- Model financial risks by generating random changes in stock prices using RAND or RANDBETWEEN.
- Simulate traffic flow by generating random car arrivals.
- Create a basic decision model where random events influence the outcome.
Wrapping Up
Using random numbers in Excel can significantly enhance your data analysis, simulations, and educational tools. From basic functions like RAND for generating numbers between 0 and 1, to RANDBETWEEN for generating integers within a specified range, to more advanced techniques like random sampling, Excel provides powerful tools to work with randomness. Whether you’re an educator looking to make engaging random quizzes, a data analyst simulating scenarios, or anyone in between, these functions can be tailored to meet a wide array of needs. With practice, you’ll find Excel’s random number generation capabilities to be indispensable in various applications.
Can I stop Excel from recalculating random numbers?
+
Yes, you can either convert the formulas to values or disable automatic calculations through the options menu to prevent Excel from recalculating random numbers.
What are some common mistakes when using random functions in Excel?

+
Common mistakes include not realizing that functions like RAND and RANDBETWEEN are volatile, misunderstanding how to control the range, and forgetting that these functions give new values each time the sheet recalculates.
Can I generate random dates in Excel?

+
Yes, by combining RANDBETWEEN with date functions like DATE, you can generate random dates within a specified range.