Mastering Ratios in Excel: Quick Guide
Understanding how to work with ratios in Excel can significantly enhance your data analysis capabilities. Ratios are fundamental in comparing numerical values, often used in financial analysis, data interpretation, and decision-making processes. This guide will walk you through the steps to calculate, manipulate, and interpret ratios using Excel's robust functions and features.
Why Ratios are Important in Excel

Before diving into the how-to, it’s crucial to understand why ratios matter:
- Comparative Analysis: Ratios allow for comparison between different datasets, which can be years, regions, or different companies.
- Financial Metrics: Ratios are the backbone of financial metrics like profitability, liquidity, and solvency ratios.
- Performance Metrics: They help measure performance over time or against benchmarks.
Setting Up Your Data


First, ensure your data is formatted correctly:
- Enter your data in columns or rows, making sure that related figures are aligned.
- Use headers for clarity. For example, if comparing revenues, use headers like “Year” and “Revenue.”
- Ensure all numbers are formatted as numbers, not text.
Calculating Ratios in Excel

Excel provides various methods to calculate ratios:
Basic Ratio Calculation
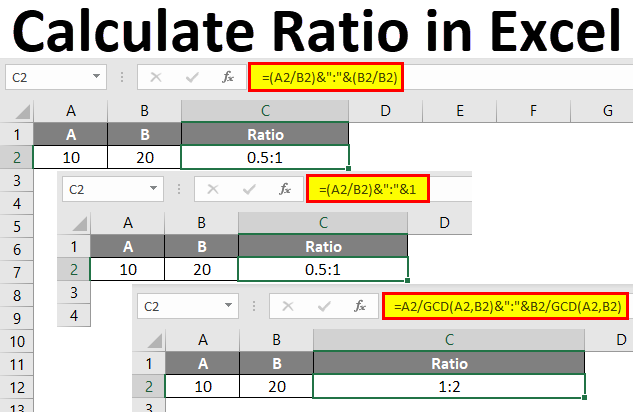
To calculate a simple ratio:
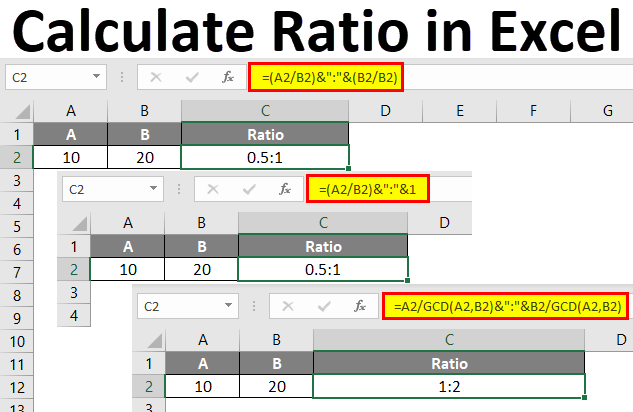
- Select the cell where you want the result to appear.
- Enter the formula:
=A2/B2assuming A2 and B2 contain your numerator and denominator, respectively. - Use the formula:
=(A2/B2)*100. - Format the cell to display the result as a percentage.
- GCD (Greatest Common Divisor): To simplify ratios, use
=GCD(A2, B2). - RATIOS Function: Not a built-in function, but you can create custom functions for specific ratios like debt-to-equity or inventory turnover.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
=Total_Liabilities/Total_Equity - Current Ratio:
=Current_Assets/Current_Liabilities - Industry benchmarks
- Historical data
- Competitors
- Plot ratios on a line or bar chart.
- Use trend lines to predict future values.
- Ratios above or below certain thresholds.
- Outliers in your dataset.
- Consistency: Always use the same time frames, accounting methods, and definitions.
- Context: Ratios mean little without context; understand the industry norms and company history.
- Documentation: Document your formulas and assumptions for transparency and reproducibility.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- Current Ratio
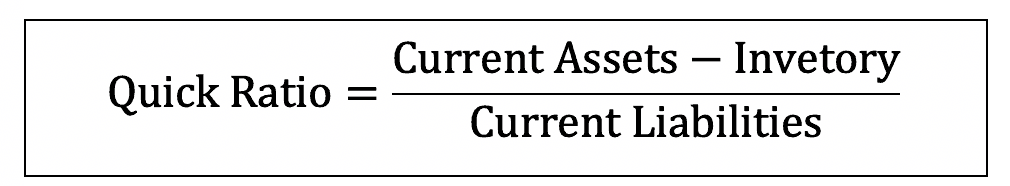
- Quick Ratio
- Return on Equity (ROE)
- Return on Assets (ROA)
- Double-check the data source for accuracy and relevance.
- Use Excel’s built-in functions for common calculations to reduce errors.
- Document all assumptions and use consistent formatting.
Percentage Ratios

If you want to express the ratio as a percentage:
Using Excel Functions for Complex Ratios
Excel offers functions for more complex calculations:
Interpreting and Using Ratios

After calculating your ratios, here’s how to interpret them:
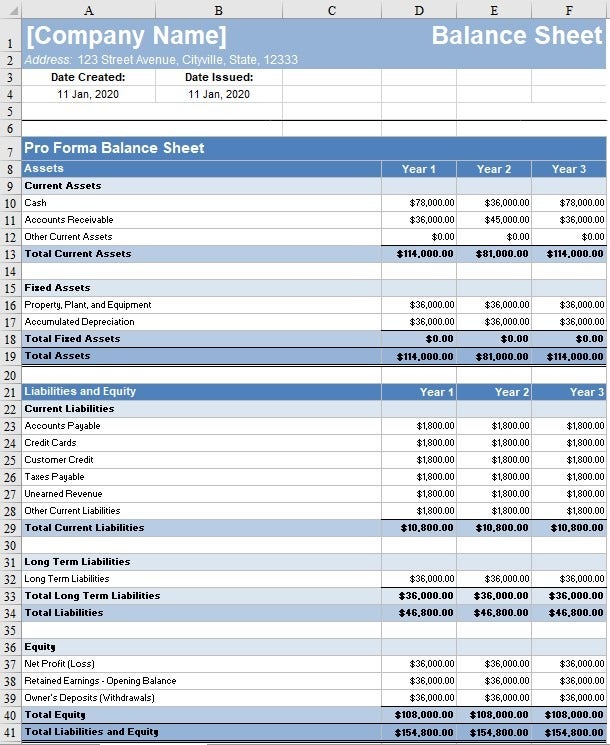
Analyzing Financial Health

Key financial ratios like:
These ratios help assess a company’s financial stability and liquidity.
Comparative Benchmarking

Comparing ratios against:
Advanced Techniques in Ratio Analysis

For those looking to delve deeper, here are some advanced techniques:
Time Series Analysis

Using Excel’s time functions to track changes:
Conditional Formatting for Visual Analysis

Use conditional formatting to highlight:
Best Practices for Ratio Analysis
Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
💡 Note: When comparing ratios, ensure that you’re comparing like with like. Differences in accounting standards or definitions can skew results.
The journey to mastering ratios in Excel is not just about learning formulas but about understanding what these numbers tell us about the underlying data. From setting up your data to advanced analysis, Excel offers a versatile platform for financial analysis, comparison, and strategic decision-making. By implementing these techniques, you can enhance your analytical skills, making your spreadsheets not just informative but insightful.
What are the most common financial ratios?

+
Some of the most common financial ratios include:
Can ratios help predict company performance?

+
Yes, ratios can provide insights into a company’s financial health, growth potential, and operational efficiency. By comparing current ratios with historical data and industry standards, analysts can make informed predictions.
How can I ensure accuracy when calculating ratios in Excel?
+
To ensure accuracy: